Research Article - Clinical Schizophrenia & Related Psychoses ( 2023) Volume 17, Issue 1
The Effect of Race, Religion and Emotional Intelligence on Academic Service Satisfaction
Radeny Ramdany1*, Alva Cherry Mustamu2 and Nur Hafni Hasim22Department of Nursing, Health Polytechnic of the Ministry of Health, Sorong, Indonesia
Radeny Ramdany, Department of Nutrition, Health Polytechnic of the Ministry of Health, Sorong, Indonesia, Email: radeny_ramdany@yahoo.com
Received: 28-Oct-2022, Manuscript No. CSRP-22-80699; Editor assigned: 31-Oct-2022, Pre QC No. CSRP-22-80699 (PQ); Reviewed: 15-Nov-2022, QC No. CSRP-22-80699 ; Revised: 21-Nov-2022, Manuscript No. CSRP-22-80699(R); Published: 10-Jan-2023, DOI: 10.3371/CSRP.RRAM.011023
Abstract
Service quality is a multidimensional driver of satisfaction. Emotional intelligence, religiosity, and race/ethnicity influence satisfaction. This research is a descriptive study with a cross-sectional approach. This study's sample was all active nursing and nutrition department students consisting of three nutrition diploma study program students, and undergraduate applied nursing students. This survey used respondent demographics, student service satisfaction questionnaires, and emotional intelligence instruments. This research was conducted online using the Google form application. Data analysis using structural equation modelling. We found that race/ethnicity, religion, and emotional intelligence did not directly or indirectly affect perceived satisfaction with educational services (p-value>0.001). However, based on the literature that has been discussed, we find that satisfaction is more influenced by skill proficiency and intellectual ability factors. We suggest that universities can increase the raw input of students with good intellect so that students and institutions can simultaneously improve services and not only be charged to institutions based on money. Future research can focus on the close relationship between intellectual ability in perceived academic service satisfaction.
Keywords
Service quality • Emotional intelligence • Satisfaction • Race • Religion
Introduction
Improving the quality of higher education must be carried out by higher education providers; both higher educations organized by the government, the private sector, and the community. Higher education, by its vision and mission, is an institution that cultivates and produces superior human resources as a bridge in producing quality products to compete in the global market. Students are a vital and central element in a university. Universities are interested in fulfilling various dimensions of satisfaction, especially for students to realize quality output in order to make the best contribution to community service. Higher education managers must have the fighting power to build a high commitment to quality improvement [1].
In its activities, higher education institutions must be able to manage their service quality system and administration. Such a scope will result in a service system that is transparent, timely, in the right quantity, and the right quality. If such aspects are carried out properly, it will create an image of reliability and assurance, which includes: trust in the implementation, timeliness of education, and guarantee of the success of education [2].
Service quality is a multidimensional driver of satisfaction. The level of service quality cannot be assessed from the company's point of view but must be viewed from the customer's point of view [3]. Satisfaction from the consumer side is seen as good if it meets what they expect. Otherwise, the service will be perceived as bad if it does not meet what they expect [4].
Customer satisfaction is expected to affect loyalty. Loyal customers can provide great benefits to the organization. The implementation of education should pay attention to the quality of service. Educational activities are not only oriented towards the result of the educational process but also through good evidence of accountability, including quality assurance, quality control, and quality improvement (National Accreditation Board for Higher Education, 1998).
Emotional intelligence is one of the factors that affect job satisfaction. Emotional intelligence as an important predictor of organizational outcomes for perceived job satisfaction. Emotional intelligence affects the effectiveness and success of an organization. This is supported by Psilopanagioti, Anagnostopoulos, Morton, and Niakas that emotional intelligence plays an important role in generating performance and job satisfaction.
Religiosity is a symbol system, belief system, value system, and symbolized behaviour system; all cantered on issues that are internalized as ultimate meaning. Someone with good religiosity will always look at every situation positively [5].
According to Diener, some factors affect satisfaction, one of which is race. There are differences in happiness and life satisfaction between white and black individuals. Black individuals tend to have lower levels of life satisfaction than white Americans.
Indonesia also has a black race, like in America, called the Melanesian race. This race lives in eastern Indonesia, Maluku, East Nusa Tenggara, and Papua. This study aims to determine the effect of race, religion, and emotional intelligence on satisfaction with academic services.
Materials and Methods
This research is a descriptive study with a cross-sectional approach. This study's sample was all active nursing and nutrition department students consisting of three nutrition diploma study program students and undergraduate applied nursing at the Health Polytechnic of the Ministry of Health, Sorong, West Papua, and Indonesia. The sampling technique used is consecutive sampling which recruits respondents based on their participation in the survey. This survey uses three questionnaires as research tools: respondent demographic data and a student service satisfaction questionnaire adopted from the university accreditation instrument in Indonesia version 3.0 [6]. While the emotional intelligence instrument was adopted [7,8]. Demographic data assessed in this study include race/ethnicity and religion. Emotional intelligence consists of 20 statements that are answered on a scale of never (1), rarely (2), sometimes (3), usually (4), and always (5). Questions numbered 1,5,912, and 15 belong to the category of self-awareness, statements numbered 3,6,10,13, and 18 are statements that assess self-management; statements number 4,7,14,17, and 19 assess social awareness, while the relationship assessment management assessed with statements numbered 2,8,11,16 and 20. Satisfaction with academic management services consisted of 15 statements with yes and no choices. This statement assesses reliability, ability, speed and responsiveness, service according to provisions, care and attention of lecturers, education staff, and study program managers in serving students, as well as adequacy, accessibility, quality, and cleanliness of facilities and infrastructure. This research was conducted online using the google form application [9,10], which was distributed via social media [11]. Data analysis used the SMART PLS structural equation modeling version 4.0 SmartPLS GmbH and Jamovi Jamovi [12,13].
Results
| Code | Variable | Frequencies | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Reliable and capable lecturer | ||
| No | 1 | 1% | |
| Yes | 95 | 99% | |
| S2 | Fast and responsive lecturer | ||
| No | 6 | 6.30% | |
| Yes | 90 | 93.80% | |
| S3 | Certainty of lecturer service | ||
| No | 7 | 7.30% | |
| Yes | 89 | 92.70% | |
| S4 | Care and attention of lecturers | ||
| No | 5 | 5.20% | |
| Yes | 91 | 94.80% | |
| S5 | Reliable and capable education staff | ||
| No | 7 | 7.30% | |
| Yes | 89 | 92.70% | |
| S6 | Fast and responsive education staff | ||
| No | 7 | 7.30% | |
| Yes | 89 | 92.70% | |
| S7 | Certainty of education staff service | ||
| No | 6 | 6.30% | |
| Yes | 90 | 93.80% | |
| S8 | Care and attention of education staff | ||
| No | 4 | 4.20% | |
| Yes | 92 | 95.80% | |
| S9 | Reliable and capable study program manager | ||
| No | 6 | 6.30% | |
| Yes | 90 | 93.80% | |
| S10 | Fast and responsive study program manager | ||
| No | 8 | 8.30% | |
| Yes | 88 | 91.70% | |
| S11 | Certainty of study program manager service | ||
| No | 7 | 7.30% | |
| Yes | 89 | 92.70% | |
| S12 | Care and attention of study program manager | ||
| No | 7 | 7.30% | |
| Yes | 89 | 92.70% | |
| S13 | Facilities and infrastructure to support the learning process | ||
| No | 7 | 7.30% | |
| Yes | 89 | 92.70% | |
| S14 | Accessibility of facilities and infrastructure | ||
| No | 8 | 8.30% | |
| Yes | 88 | 91.70% | |
| S15 | Quality of facilities and infrastructure | ||
| No | 6 | 6.30% | |
| Yes | 90 | 93.80% |
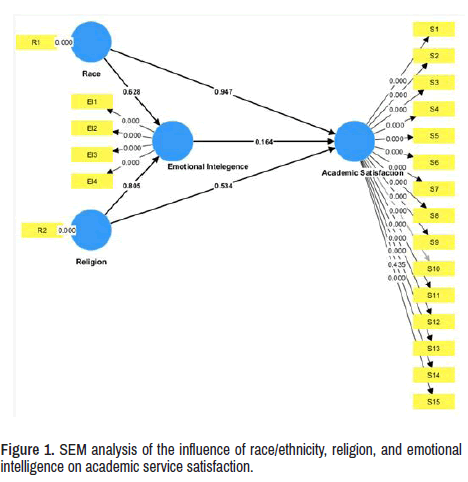
Figure 1 shows that race/ethnicity, religion, and emotional intelligence do not directly or indirectly affect the perception of satisfaction with educational services (p-value>0.001).
Discussion
Improving the quality of higher education is a necessity that must be carried out by higher education providers, both higher educations organized by the government and the community. The quality of education achieved so far is not sufficient for college graduates. This can be proven by the weak competitiveness of Indonesian university graduates in the international arena.
In some universities, the role of lecturers is to provide satisfaction to students in learning so that the costs incurred by students are commensurate with what is obtained. While the availability of learning facilities also affects student satisfaction with the costs that have been incurred. Learning facilities in universities should use better facilities because students are figures who grow as individuals and have self-concept maturity, moving from dependence. The maturity in question is the psychological maturity of students as individuals who can direct themselves.
Encourage the emergence of psychological needs, namely the desire to be seen and treated by others as a person who directs himself, not directed, forced, or manipulated by others. Maturity level is one of the factors that encourage students to give a perception of something they can feel while being a student. Some students are quite happy with the situation they felt while being a student, both in terms of the learning process, campus facilities, the environment, and current campus life. However, some students feel less or dissatisfied with the learning process, campus facilities, environment, and campus life, so that dissatisfaction arises in them.
Students, in this case, can be said to be college customers with relatively complex and diverse characteristics. Hence, customers are not only single but have many parties with different factors or satisfaction criteria. One of the customers at the university, in this case, a student, is more suitable to be identified with the term stakeholder because it shows that there are many customers with different satisfaction factors from one another. Other types of higher education stakeholders include graduate users (end users), society (social), as well as lecturers, and employees (employees).
Intellectual intelligence, emotional intelligence, and spiritual intelligence are one of the factors that can affect the view of satisfaction. This study's results differ from previous studies, which found that emotional, intellectual, and spiritual intelligence significantly affected performance [14]. This reason may be answered through research [15] which suggests that satisfaction has more to do with skills. In addition, it is corroborated by the research results [16] that the perception of satisfaction will be high if the person has high skills.
If we review again that skills appear when someone has the ability. Skills can also involve intellectual skills [17] and these intellectual skills appear when a person has sufficient knowledge.
One of the factors that cause loyal consumers is the result of customer satisfaction. Consumer satisfaction has several dimensions, namely the quality of service products, the convenience of procedures, and customer support who are students [18]. This study found that almost all students perceived satisfaction with the services of lecturers, education staff, learning support facilities, and infrastructure. Moreover, this is not influenced directly or indirectly by the tendency of religious factors, race, and emotional intelligence.
Race, religion, and intelligence are psychological and psychological factors, while perception is related to intelligence skills and abilities. A study Skarupski et al. found that racial differences in life satisfaction were almost non-existent [19]. However, at lower levels of spiritual experience, older African Americans showed lower levels of life satisfaction than older whites. This pattern suggests that spiritual experiences are a positive source of enabling older African Americans to cope with decreased life satisfaction and that lower spiritual experiences may be particularly harmful to older African Americans' life satisfaction. This illustrates that, indeed, in perceiving satisfaction in academic services, racial and religious differences have no effect.
Conclusion
In this study, we found that race, religion, and emotional intelligence have no direct or indirect relationship to perceptions of the quality of university academic services. However, based on the literature that has been discussed, we find that satisfaction is more influenced by skill proficiency and intellectual ability factors. We suggest that universities can increase the raw input of students with good intellect so that students and institutions can simultaneously improve services and not only be charged to institutions based on money. Future research can focus on the close relationship between intellectual ability in perceived academic service satisfaction.
References
- Marthalina, Marthalina. "Analisis Kualitas Pelayanan Akademik Dan Kepuasan Mahasiswa Di Ipdn Kampus Jakarta." Jurnal MSDM (2018): 1-18.
- Djumara, SN. “Kualitas Kinerja Pelayanan Akademik Stia Lan Bandung.” Jurnal Ilmu Administrasi. 10 (2013).
- Widawati, Etty. "Analisis Tentang Kepuasan Mahasiswa Terhadap Pelayanan Akademik Dan Pelayanan Administrasi." Jurnal Mitra Manajemen 4 (2020): 1500-1513.
- Rinala, I. Nyoman, I. Made Yudana and I. Nyoman Natajaya. "Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan Akademik Terhadap Kepuasan dan Loyalitas Mahasiswa Pada Sekolah Tinggi Pariwisata Nusa Dua Bali." Jurnal Administrasi Pendidikan Indonesia 4 (2013).
- Jannah, Elsa Rohmatul. "Hubungan Antara Religiusitas dan Persepsi Terhadap Kesehatan dengan Kebahagiaan Pada pria Yang Menikah Diusia Dewasa Awal." UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 2017.
- Tinggi, Badan Akreditasi Nasional Perguruan and status akreditasi dan peringkat terakreditasi. "Badan Akreditasi Nasional Perguruan Tinggi." (2018).
- Feldman, Daniel A. The handbook of emotionally intelligent leadership: Inspiring others to achieve results. Leadership Performance Solutions Press. 1999.
- Sterrett, Emily A. The manager's pocket guide to emotional intelligence: From management to leadership. Human Resource Development, (2000).
- Google. Google Forms: Online Form Creator | Google Workspace. (2022).
- Mustamu, A.C. Kuesioner Penelitian. (2022).
- WhatsApp LLC. WhatsApp. WhatsApp.com. (2022).
- SmartPLS GmbH. SmartPLS. (2022).
- Jamovi. (2021).
- Wibowo, Cahyo Tri. "Analisis Pengaruh Kecerdasan Emosional (EQ) Dan Kecerdasan Spiritual (SQ) Pada Kinerja Karyawan." J Business and Management 15 (2015): 1-16.
- Todd, Samuel Y., Kenneth J. Harris, Ranida B. Harris and Anthony R. Wheeler. "Career Success Implications of Political Skill." J Soc Psychol 149 (2009): 279-304.
- Breland, Jacob W., Darren C. Treadway, Allison B. Duke and Garry L. Adams. "The Interactive Effect of Leader-Member Exchange and Political Skill on Subjective Career Success." J Leadership & Organizational Studies 13 (2007): 1-14.
- Nasihudin, Nasihudin and Hariyadin Hariyadin. "Pengembangan Keterampilan dalam Pembelajaran." Jurnal Pendidikan Indonesia 2 (2021): 733-743.
- Sari, Nilam Pusvita, Darwin Lie, Marisi Butarbutar and Ady Inrawan. "Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan Dan Persepsi Konsumen Terhadap Loyalitas Konsumen Dengan Kepuasan Konsumen Sebagai Variabel Intervening Pada Eka Prima Motor Pematangsiantar." SULTANIST: Jurnal Manajemen dan Keuangan 5 (2017): 26-37.
- Skarupski, Kimberly A., George Fitchett, Denis A. Evans and Carlos F. Mendes de Leon. "Race differences in the association of spiritual experiences and life satisfaction in older age." Aging Ment Health 17 (2013): 888-895.
Citation: Ramdany, Radeny, Alva Cherry Mustamu and Nur Hafni Hasim. “The Effect of Race, Religion and Emotional Intelligence on Academic Service Satisfaction.” Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses 17 (2023). Doi: 10.3371/CSRP.RRAM.011023.
Copyright: © 2023 Ramdany R, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.