Research Article - Clinical Schizophrenia & Related Psychoses ( 2021) Volume 0, Issue 0
Impact of DNA Repair System Genes RAD-18 and XRCC1 Polymorphism in Depression Disorders Patients
Mona N Al-Terehi1*, Zahraa Haleem AlQaim2 and Arafat Hussein Aldujaili32Department of Medical Laboratories, Al-mustaqbal University, Babylon, Iraq
3Department of Medicine, Kufa University, Kufa, Iraq
Mona N Al-Terehi, Department of Sciences, University of Babylon, Babylon, Iraq, Email: Monanajah1981@gmail.com
Received: 04-Aug-2021 Accepted Date: Aug 18, 2021 ; Published: 25-Aug-2021
Abstract
The Depressive Disorders (DDs) it is one of the most widespread psychiatric pathology forms and the relation of DNA repair with DD still under investigation, the present study was conducted to detect the RAD-18 Arg302Gln (rs373572) and XRCC1 Arg399Gln (28152) G>A gene polymorphisms in the DD patients, allele specific PCR and PCR-CTTP were used, the results show the age of patients (38.10 ± 12.74) year with BMI (24.98 ± 3.96) kg/m2 have duration of disease (7.50 ± 7.70) years and of control was (38.36 ± 12.85) year with BMI (27.02 ± 4.44) Kg/m2, non-significant differences of family history and significant variations were observed to dietary and exercise in study groups. The genotyping The RAD-18 show two alleles (A and G) and two genotyping (AA and GG), the AA was found in all patients and in 92% of the control group, GG found in 8% of the control group and didn’t find in patients in non-significant differences (Od 0.2410, CI% 0.0109- 5.3247, P 0.36), there was non-significant differences in compare GA and GG genotyping (Od 17.000, CI% 0.13- 2166.90, P 0.25). the allele observed in patients (1) but G didn’t appear , in control group A was 0.92% in control and G found in 0.08. There were non- significant differences of allele frequency (Od 0.2410, CI% 0.010 -5.324, P 0.367). The XRCC1 genotyping show two alleles (A and G) and three genotyping (AA, GG and AG), the GG was less frequent in patients than the control group (26.31%, 44%), GA was more frequent in patients group (73.68%) than control group (48%) in non-significant differences (Od 2.2000 CI% 0.605- 7.999, P 0.231), AA observed in 8% of control group but didn't observe in patients group in non-significant differences (Od 5.8000, CI% 0.253-132.56, P 0.270), finally the alleles frequency show that G allele observed in 0.63 and 0.68 in patients and control group respectively also 0.36 and 0.32 of A allele in non-significant differences (Od 1.2396, CI% 0.3534-4.3484, P 0.737). the present study concluded that no-association between repair genes RAD-18 and XRCC1 with DD disease.
Keywords
DNA repair • Gene polymorphism • Depression • Patients
Introduction
Depressive Disorders (DDs) it is one of the most widespread psychiatric pathology forms, about 264 million were recorded as a DD in the world according to WHO, its represent by 3% in Japan and 16.9 in USA while its range (8-12)% in other countries [1,2]. The DD impact in the life quality and the long period of depression let to attempted suicide, however the mechanism of DD development still under investigations, several studies deal with family and twin pointed to contributed genetic factors in depression etiology in addition to Heritability and the lase effected by maternal or paternal inherited [3-7] .The DNA repair is an important system which play major role in genome stability and mutation repair, there are some encoded to proteins contribution in different repair activities, present study deal with RAD-18 gene encoded to E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase used in post replication repair of UV-damaged DNA, by filling the gap of new strand, other function is forming UBE2B-RAD18 ubiquitin ligase complex used in mono-ubiquitination of DNA-associated PCNA on 'Lys-164'. Has ssDNA binding activity by linked the E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2B [8- 10].
The other gene in present study is X-Ray Cross-Complementing Group 1 (XRCC1), it is one of the Base Excision Repair (BER) protein pathways, the Polymorphisms have been found to be associated with DNA repair capacity changes that caused some diseases [11].
The Studies deal with the association repair genes with DD were little and need more investigation, thus the present study was suggested.
Methodology
Study sitting and sample collection
A case –control study was conducted in the DNA lab of bio-Dep/ Babylon Uni. 20 DD and 20 apparently healthy individuals were contributed in the present study, patients were attended to psychiatric clinic in Al-Hakeem hospital who diagnostic as a DD by specialist Prof Dr. Arafat Al-Dujaily, blood samples were collected from patients and control, according to ethical approval of Environment and health ministry in Iraq with written consent from all contributors.
Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria included (female, diabetes mellitus, cancers infected, viral infected, and smokers).
DNA extraction and primer design
The DNA was extracted according to manufacture of the kit which provided by favorgen company, then purity and concentration were determined using Nano-drop, the primers were selected according to previous studies and it virtual amplified to confirm the products sizes, Oligos were provided by macrogene company, stock and aliquot solution were prepared according to manufacture leaflet. The RAD-18 Arg302Gln (rs373572) was detection using allele specific PCR by following primers: F1: 5’-ATA CCC ATC ACC CAT CTT C and R1, GTC TTCTCT ATA TTT TCG ATT TCT T for the Gln allele (146 pb) , F2, TTA ACA GCT GCT GAA ATAGTT CG and R2, CTG AAA TAG CCC ATT AAC ATA CA (106 bp) Arg allele. A 206 bp band was common band the XRCC1 Arg399Gln (28152) G>A polymorphism was implemented using PCR with Confronting Two-Pair Primers Method (PCRCTTP) [12,13]. F1 TCC CTG CGC CGC TGC AGT TTC T; R1 TGG CGT GTG AGG CCT TAC CTC C ; F2, TCG GCG GCT GCC CTC CCA; and R2 AGC CCT CTG TGA CCT CCC AGG C, the G allele (399Arg), A allele (399Gln) amplify bands have 447- and 222-bp respectively and 630-bp common band [14].
Amplification conditions
The conditions of target SNPs were amplified using the following programs, for the RAD-18 Arg302Gln (rs373572) 95ºC- 5 min for one time then for 30 S for 30 times with annealing tm 58ºC for 30 min, and extension 72ºC for 30 S and for 10 min in the last step of amplification. the XRCC1 amplification conditions were 95ºC- 5 min for one time then for 30 S for 30 times with annealing tm 59ºC foe 30 S, and extension 72ºC for 30 S and for 10 min at 72ºC in final extension step.
Electrophoresis
The allele specific PCR of RAD-18 and PCR-CTTP of XRCC1 products were visualized by electrophoresis using agaros gel (1%, 70 V, 20 mA for 45 min), gel was staining by ethidium bromide, according to biosafety approval. then gel documented using photo-documentation tool.
Statistical analysis
The genotyping and socio-demographic distribution analysis using Odd ratio (CI95%) at P<0.05. allele frequency was calculated according to hardy-wienberig equilibrium (p+q=1).
Results and Discussion
The present findings show that the mean of patient's age was (38.10 ± 12.74) year with BMI (24.98 ± 3.96) kg/m2 and theses patients have duration of disease (7.50 ± 7.70) years. In the control group the mean of age was (38.36 ± 12.85) year with BMI (27.02 ± 4.44) Kg/m2. Family history of disease, both age and BMI non-significant differences, there was 20% of patients have a Family History (FH) of disease while 10% of control individuals was positive to FH in non-significant differences (Od 2.2500, CI% 0.3623-13.9720, P=0.3841), the exercise also detection, 20% of patients were doing exercise and 65% of the control group in significant differences (Od 7.4286, CI% 1.7778-31.0408, P=0.0060). The dietary of study contributors was enrolled, significant differences was observed (Od 12.6667, CI% 1.4022-114.4240, P=0.0238) between patients and the control group which were under dietary (5% and 40%) respectively (Table1).
| Subjects | Patients | Control | Statistic | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 38.10 ± 12.74 | 38.36 ± 12.85 | 0.0626 | 0.9504 |
| BMI kg/m2 | 24.98 ± 3.96 | 27.02 ± 4.44 | 0.1437 | 1.4946 |
| Duration (year) | 7.50 ± 7.70 | 0 | ||
| Family history Yes No |
20% 80% |
10% 90% |
2.2500 (0.3623 - 13.972) |
0.3841 |
| Exercise Yes no |
20% 80% |
65% 35% |
7.4286 (1.7778 - 31.040) |
0.0060 |
| Dietary Yes No |
5% 95% |
40% 60% |
12.6667 (1.402 - 114.424) |
0.0238 |
The depression disorder has been the most problem health in Iraq in the last decade, several factors interacted to incidence disease like genetic factors, life style, The way of thinking and the type of problems that a person encounters in life, the socio-distribution of present subjects that deal with some lifestyle variation show that the dietary and exercise were significant association with DD and this agree with Belvederi Murri the family history also affected but in non- significant association, studies exhibited the role of family history in depression development [15,16]. Furthermore COVID-19 pandemic and quarantine in the last two years contributed in people's mental health [17].
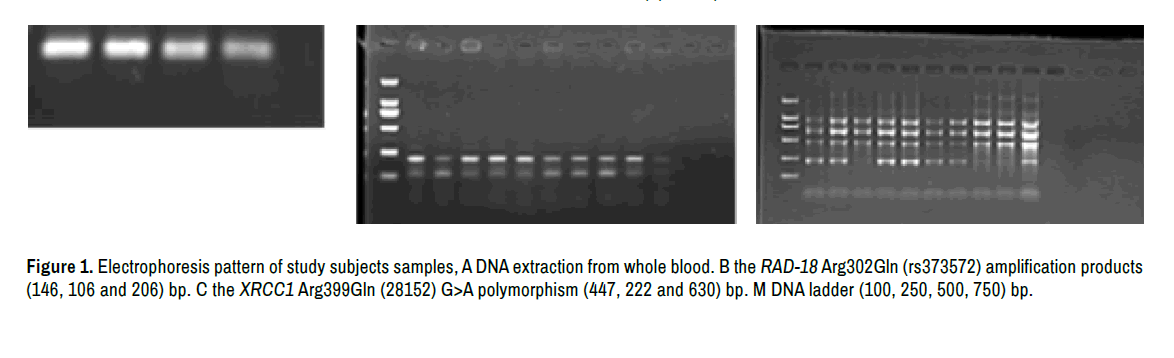
The DNA extracted from whole blood show high purity and concentration ranged (50-150) ng/μl (Figure1A) the amplification products of targeted SNPs were successful and produced optimum size (Figure 1B and 1C).
The RAD-18 Arg302Gln (rs373572) genotyping show two alleles (A and G) and two genotypes (AA and GG), the AA was found in all patients and in 92% in the control group while GG found in 8% of the control group and didn’t find in patients in non-significant differences (Od 0.2410, CI% 0.0109- 5.3247, P=0.36), the GA didn’t observe in present study, This is non-significant differences in comparing with GG genotyping (Od 17.000, CI% 0.13- 2166.90, P=0.25). The allele frequency was calculated A allele observed in patients (1) but G didn’t find, in the control group A was observed in 0.92 in the control and G found in 0.08. There were nonsignificant differences of allele frequency (Od 0.2410, CI% 0.010 -5.324, P 0.367) (Table 2).
| Genotyping | Patients (%) | Control (%) | Odd ratio (CI95%) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAD-18 Arg302Gln (rs373572) | ||||
| Arg/Arg (AA) |
100% | 92% | 0.2410 (0.0109- 5.3247) |
0.3676 |
| Gln/Gln (GG) | 0 | 8% | ||
| Arg/Gln (AG) |
0% | 0% | 17.000 (0.13- 2166.90) |
0.2520 |
| A | 1 | 0.92 | 0.2410 (0.010 -5.324) |
0.3676 |
| G | 0 | 0.08 | ||
| XRCC1 Arg399Gln (28152) G>A | ||||
| Arg/Arg (GG) |
26.31% | 44% | 2.2000 (0.605- 7.999) |
0.2312 |
| Arg/Glu (GA) |
73.68% | 48% | ||
| Gln/Gln (AA) |
0 | 8% | 5.8000 (0.253-132.56) |
0.2709 |
| G | 0.63 | 0.68 | 1.2396 (0.3534-4.3484) |
0.7373 |
| A | 0.36 | 0.32 | ||
The XRCC1 Arg399Gln (28152) G>A genotyping showed two alleles (A and G) and three genotyping also (AA, GG and AG), the GG was less frequent in patients than control group (26.31%, 44%) respectively, GA was more frequent in the patients group (73.68%) than control group (48%) in nonsignificant differences (Od 2.2000 CI% 0.605- 7.999, P=0.231), AA observed in 8% of the control group but didn't find in patients group in non-significant differences (Od 5.8000, CI% 0.253-132.56, P=0.270), finally the allele frequency show that the G allele observed in 0.63 and 0.68 in patients and control group respectively also 0.36 and 0.32 for A allele in non-significant differences (Od 1.2396, CI% 0.3534-4.3484, P=0.737).
The RAD-18 gene encoded to E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase used in DNA repair and its studied as a result of long war times in Iraq at the end of 20 and began 21 century [9], the present study show non-significant association between DD and RAD-18 gene this may be because the patients didn’t exposure to ionized RADiation, Chen et al. [18] found increasing the RAD- 18 level in human giloma cells exposure to ionizing RADiation and when RAD-18 gene was knockdown; cells directed to apoptosis pathway. On the other hand studies proved the role of DNA repair role during Neural Development because any mutations or unpaired lesions may be led to mis-function and huge effect and disease in nervous system [19, 20]. Investigators found increased DNA damage level in DD patients and this caused to elevation in repair system activity levels of different enzymes and proteins contributed in DNA repair processes, however we found elevation in the 8-oxodeoxygunine in DD patients (data not shown), however, there was poor information's about RAD-18 relation with DD [21].
The X-Ray Cross-Complementing Group 1 (XRCC1) is one of the Base Excision Repair (BER) protein pathway and the Polymorphisms have been found associated with DNA repair capacity changes that caused some disease like mental health disorders [22] , the present finding show non-significant association between XRCC1 Arg399Gln (28152) G>A polymorphism and DD patients, studies exhibited that there was strong relation and a potential candidate contributing to the etio-pathogenesis of the Schizophrenia diseases, the studies deal with molecular dynamics clarified the mutation (Arg399Gln) role in the structural and functional properties changes of the XRCC1 protein which cause malfunction and contribute in the vulnerability to the disease. Further the oxidative stress and disorders in DNA damage repair mechanisms contribute to elevated levels of DNA lesions observed in depression, a study conducted by Czarny et al. that studied several SNPs in repair gene included XRCC1 [23,24]. In a another study Celik et al, didn’t find association between XRCC1 Arg399Gln with obsessive-compulsive disorder [25,26].
Conclusion
The Depressive Disorders (DDs) it is one of the most widespread psychiatric pathology forms and the relation of DNA repair with DD still under investigation, the present study was conducted to detect the RAD- 18 Arg302Gln (rs373572) and XRCC1 Arg399Gln (28152) G>A gene polymorphisms in the DD patients, allele specific PCR and PCR-CTTP were used, the results show the age of patients. Investigators found increased DNA damage level in DD patients and this caused to elevation in repair system activity levels of different enzymes and proteins contributed in DNA repair processes, however we found elevation in the 8-oxodeoxygunine in DD patients (data not shown), however, there was poor information's about RAD-18 relation with DD.
References
- Flint, Jonathan and Kenneth S Kendler. “The Genetics of Major Depression.” Neuron 81 (2014): 484-503.
- James, Spencer L, Degu Abate, Kalkidan Hassen Abate and Solomon M Abay, et al. “Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.” Lancet 392 (2018): 1789–1858.
- Sullivan, Patrick F, Michael C Neale and Kenneth S Kendler. “Genetic Epidemiology of Major Depression: Review and Meta-Analysis.” Am J Psychiatry 157 (2000): 1552-1562.
- Kendler, Kenneth S, CO. Gardner, MC. Neale and CA. Prescott. “Genetic Risk Factors for Major Depression in Men and Women: Similar or Different Heritabilities and Same or Partly Distinct Genes?.” Psychological Med 31 (2001): 605-616.
- Menke, Andreas and Elisabeth B Binder. “Epigenetic Alterations in Depression and Antidepressant Treatment.” Dialogues Clin Neurosci 16 (2014): 395.
- Al-Terehi, Mona N, and Ayad F Alkaim. “Role of Nanoparticles Applications as a Model in DNA Technologies; A Review.” India J Forensic Med Toxicology 13 (2019): 855-860.
- Al-Terehi, Mona N, Ayad F Alkaim and Abubakar Yaro. “An in Silico Approach to Design Potential siRNA Molecules of SARS-CoV-2 Virus Structural Genes, a Preliminary Opinion for COVID-19 Inhibition.” Annals Tropical Med Public Health 23 (2020): 23-111.
- Unk, Ildiko, Ildikó Hajdú, Károly Fátyol and Barnabás Szakál, et al. “Human SHPRH is a Ubiquitin Ligase for Mms2–Ubc13-Dependent Polyubiquitylation of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen.” Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103 (2006): 18107-18112.
- Cotta-Ramusino, Cecilia, E Robert McDonald, Kristen Hurov and Mathew E Sowa, et al. “A DNA Damage Response Screen Identifies RHINO, a 9-1-1 and TopBP1 Interacting Protein Required for ATR Signaling.” Science 332 (2011): 1313-1317.
- Alabdali, Yasir Adil Jabbar, Hawraa F Wali and Ayad F Alkaim. “ZnO Nanoparticles Activity Against the Virulence Gene of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated from Patients with Burn Wounds Infection in Al Muthanna Population.” Annals Tropical Med Public Health 23 (2020): 470-479.
- Hanssen-Bauer, Audun, Karin Solvang-Garten, Mansour Akbari and Marit Otterlei. “X-ray Repair Cross Complementing Protein 1 in Base Excision Repair.” Int J Mol Sci 13 (2012): 17210-17229.
- Das, Sambuddha, Sukanya Purkayastha, Hirakjyoti Roy and Anima Sinha, et al. “Polymorphisms in DNA Repair Genes Increase the Risk for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension.” Biomol Concepts 9 (2018): 80-93.
- Hamajima, Nobuyuki, Toshiko Saito, Keitaro Matsuo and Ken‐ichi Kozaki, et al. “Polymerase Chain Reaction with Confronting Two‐Pair Primers for Polymorphism Genotyping.” Jpn J Cancer Res 91 (2000): 865-868.
- Ito, Hidemi, Keitaro Matsuo, Nobuyuki Hamajima and Tetsuya Mitsudomi, et al. “Gene–Environment Interactions Between the Smoking Habit and Polymorphisms in the DNA Repair Genes, APE1 Asp148Glu and XRCC1 Arg399Gln, in Japanese Lung Cancer Risk.” Carcinogenesis 25 (2004): 1395-1401.
- Belvederi Murri, Martino, Panteleimon Ekkekakis, Marco Magagnoli and Domenico Zampogna, et al. “Physical Exercise in Major Depression: Reducing the Mortality Gap while Improving Clinical Outcomes.” Front Psychiatry 9 (2019): 762.
- Zalar, B, A Blatnik, A Maver and Z Klemenc-Ketiš, et al. “Family History as an Important Factor for Stratifying Participants in Genetic Studies of Major Depression.” Balkan J Med Genet 21 (2018): 5.
- Bueno-Notivol, Juan, Patricia Gracia-García, Beatriz Olaya and Isabel Lasheras, et al. “Prevalence of Depression During the COVID-19 Outbreak: A Meta-Analysis of Community-Based Studies.” Int J Clin Health Psychol 21 (2021): 100196.
- Xie, Chen, Hongwei Wang, Hongbin Cheng and Jianhua Li, Zhi Wang, et al. “RAD18 Mediates Resistance to Ionizing RADiation in Human Glioma Cells.” Biochem Biophys Res Commun 445 (2014): 263-268.
- McKinnon, Peter J. “Maintaining Genome Stability in the Nervous System.” Nat Neurosci 16 (2013): 1523-1529.
- Madabhushi, Ram, Ling Pan and Li-Huei Tsai. “DNA Damage and its Links to Neurodegeneration.” Neuron 83 (2014): 266-282.
- Czarny, Piotr, Dominik Kwiatkowski, Dagmara Kacperska and Daria Kawczyńska, et al. “Elevated Level of DNA Damage and Impaired Repair of Oxidative DNA Damage in Patients with Recurrent Depressive Disorder.” Med Sci Monit 21 (2015): 412.
- Sujitha, SP, D Thirumal Kumar, C George Priya Doss and K Aavula, et al. “DNA Repair Gene (XRCC1) Polymorphism (Arg399Gln) Associated with Schizophrenia in South Indian Population: A Genotypic and Molecular Dynamics Study.” PLoS One 11 (2016): e0147348.
- Czarny, Piotr, Dominik Kwiatkowski, Monika Toma and Joanna Kubiak, et al. “Impact of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Base Excision Repair Genes on DNA Damage and Efficiency of DNA Repair in Recurrent Depression Disorder.” Mol Neurobiol 54 (2017): 4150-4159
- Celik, Ramazan, Elif Sinem Iplik, Cem Ismail Kucukali and Erdem Tuzun, et al. “Investigation of DNA Repair Genes in Patients with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.” Adv Clin Exp Med 26 (2017): 1269-1273.
- Munizza, Carmine, Piergiorgio Argentero, Alessandro Coppo and Giuseppe Tibaldi, et al. “Public Beliefs and Attitudes Towards Depression in Italy: A National Survey.” PLoS One 8 (2013): e63806.
- McGuffin, Peter, Sarah Cohen and Jo Knight. “Homing in on Depression Genes.” 164 (2007): 195-197.
Citation: Al-Terehi, Mona N, Zahraa Haleem Alqaim and Arafat Hussein Aldujaili. "Impact of DNA Repair System Genes RAD-18 and XRCC1 Polymorphism in Depression Disorders Patients." Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses 15(2021). Doi:10.3371/CSRP.AMZH.11.12.21.
Copyright: © 2021 Al-Terehi MN, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.